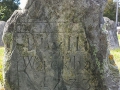African Burial Customs
One surviving aspect of African custom and culture in early America is the custom of funeral and burying rituals. In Newport, both the enslaved and free African community, largely coming from what is today Ghana, would provide elaborate funerals for their dearly departed. The funeral was as much a celebration of life as it is a bid farewell to the dead. Most importantly it signified the departure of souls in their next journey to join their ancestors.
On May 18th, 1770, 70 year old Quash Dunbar died. In his diary on May 20th of that same year, Rev. Ezra Stiles wrote:
“A Negro Burying, the Church bell tolled (all our Bells sometimes toll for Negroes), a procession of Two Hundred Men and One Hundred & Thirty Women Negroes.”
The funeral often included dancing, singing and public recognition of the relevance of the life of the departed. In an African funeral in Newport, the leaders of the community would lead a procession with the body on a wagon from the center of the town to the burying grounds. The procession would be organized by a ceremonial undertaker, a well-respected position within the African community.
Click here to learn about Mintus the
“Last Colored Undertaker” of Newport and how he presided over 18th century burials in God’s Little Acre.
Burial Markers in God’s Little Acre